
Due to their ability to generate very powerful magnetic fields, low resistance and high efficiency, electromagnets have often been applied in medicine and scientific equipment. This sector has experienced significant growth in recent years.
This is why, today, electromagnets in medicine play a key role in advanced treatments, such as hyperthermia treatments for cancer, implants and magnetic resonance imaging, to mention just three of the areas of greatest use.
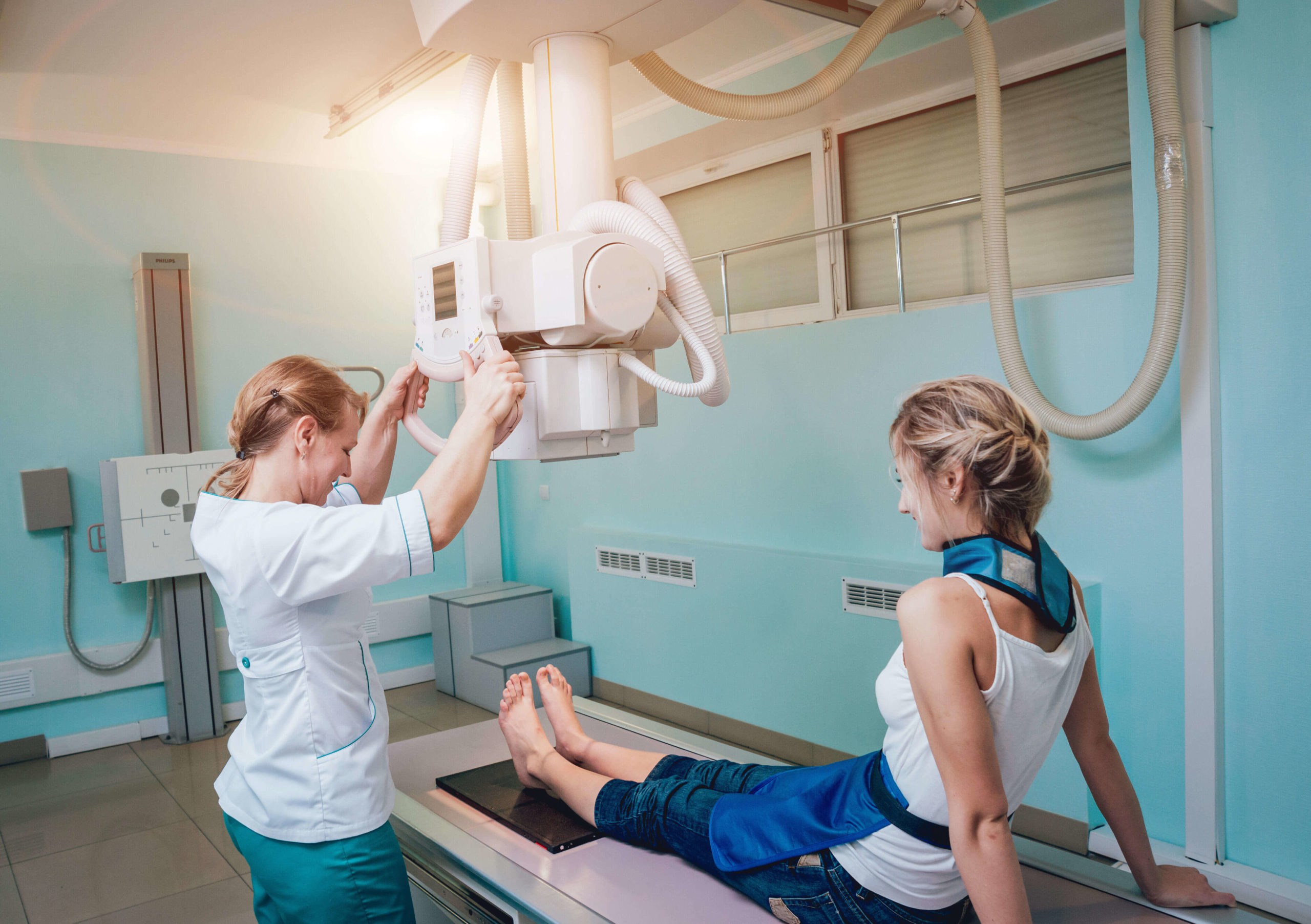
But beyond all the applications of electromagnets in medicine, the most important use of these in hospitals is in magnetic resonance imaging, commonly known as MRI.

It is used to get a detailed picture of the inside of the body, which helps diagnose a number of diseases. MRI can be used to diagnose brain tumors, hemorrhage, nerve injury, and stroke injury and can also detect if the heart or lungs are damaged.
In fact, studies have found that if the device generated static magnetic fields of 300 to 500 Gauss over a pain activation point, the application of the electromagnet provided immediate relief to the subjects.
This involves placing a powerful electromagnet in the patient's head and the electromagnet passes a current through the scalp to the underlying neurons. Patients treated with this have shown improvement with respect to depression, mania, Parkinson's disease and such disorders.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is now considered a diagnostic tool with high potential, but more studies are needed before its safety can be guaranteed.
Today there are countless uses for electromagnets, such as the application of electromagnets in industrial robotics, which is closely linked to medicine.
Electromagnets integrate median and robotics using the tools of a surgeon, such as an eye surgeon, who can extract steel pieces from a patient's eye with an electromagnet, increasing the current until he pulls enough to gently remove the metal.
Also, in microsurgery researchers are working on electromagnets that can move micro-robots around the body to perform the surgery without opening the patient.
Electromagnets are devices that work because an electric current produces a magnetic field, and if a wire carrying an electric current is formed in a series of loops, the magnetic field can concentrate inside the loops.
But if you want to know more about them, at IMA we can make it clear why electromagnets heat up, as well as help you choose the type of magnet that best suits your needs. If you have any questions, ask us.