Morisky Medication Adherence Scale-8
The Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) is an 8-item structured, self-report measure that assesses medication adherence.
Link to Instrument
Acronym MMAS-8
Cost
Cost Description
Users must contact the author for pricing and licensing
Diagnosis/Conditions
- Arthritis + Joint Conditions
- Cardiac Dysfunction
- Diabetes
Populations
Key Descriptions
- Questions 1-7 require a dichotomous reply from the patient and address common reasons for missing medications
- 8th question is answered using a 5-point Likert scale regarding how often the individual has difficulty remembering to take medicine
- Scores are summed and range from 0-8
- Specific scoring and administration guide is only available with written permission and approved license from the author
Number of Items
Time to Administer
Required Training
No Training
ICF Domain
Considerations
License requests to use the MMAS-8 should be made via e-mail to dmorisky@gmail.com.
Cost for use of the scale upon licensing approval is not readily known and may limit clinical utility.
MMAS Research, LLC, states that the scale is available in 80 different languages (Morisky, 2017). This along with its brevity improve its utility.
Users should note that known psychometric properties differ across translations and populations.
Musculoskeletal Conditions
Standard Error of Measurement (SEM)
Osteoporosis (Reynolds et al., 2014; n = 400; mean age = 71.6 (8.6) years; post-menopausal females)
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
Osteoporosis (Reynolds et al., 2014)
- 2.05 (calculated from given statistics)
Test/Retest Reliability
Osteoporosis (Reynolds et al., 2014; n = 400; mean age = 71.6 (8.6) years; post-menopausal females)
- Excellent test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.83)
Internal Consistency
Osteoporosis (Reynolds et al., 2014; OP)
- Adequate internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.74
Criterion Validity (Predictive/Concurrent)
Predictive Validity:
Osteoporosis (Reynolds et al., 2014; OP)
- Sensitivity: 81.5% for predicting those with low/medium adherence
- Specificity: 45.7% for predicting those with high adherence
Arthritis
Standard Error of Measurement (SEM)
Gout (Tan et al., 2016; n = 91; mean age = 53.5 (16.9) years)
- SEM = 0.98 (calculated from given statistics)
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
Gout (Tan et al., 2016)
- 2.74 (calculated from given statistics)
Test/Retest Reliability
Gout (Tan et al., 2016; n = 18; 20% of sample; age not given for subset)
- Adequate test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.70)
Internal Consistency
Gout (Tan et al., 2016; Gout)
- Adequate internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.73)
Mental Health
Internal Consistency
Psychiatric Outpatient (De las Cuevas & Peñate, 2015; n = 967; mean age = 49.6 (13.8) years; Spanish version)
- Adequate internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.75)
Criterion Validity (Predictive/Concurrent)
Predictive Validity:
Psychiatric Outpatient (De las Cuevas & Peñate, 2015; Spanish version)
- Significant correlations with positive attitudes of patients toward their treatment, revealing that as patients become more satisfied with their medication they start to better understand how the treatment is helping them and increase their adherence. (F (2, 948) = 41.7; p = .000), with a moderate effect size (.081)
Construct Validity
Convergent Validity:
Psychiatric Outpatient (De las Cuevas & Peñate, 2015; Spanish version)
- The structure obtained a Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin coefficient of .83, with a Chi square (28) = 875.68, p = .000. Results showed a two-factor solution, but results tended to a one-factor solution: using an item selection criterion of > 0.30 loading coefficients, only item #7 did not fall within the one-factor solution.
- Able to differentiate between 5 major groups of disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, depression, anxiety, personality disorders). F (4, 932) = 6.35; p = .000; effect size = .027.
Cardiovascular Disease
Standard Error of Measurement (SEM)
Hypertension
- SEM = 0.81 (Muntner et al., 2011; n = 210; mean age = 78.1 (5.8) years)
- SEM = 0.42 (Kim et al., 2014; n = 109; mean age = 57.2 (11.2) years; HTN; Korean version; SEM calculated from given statistics)
- SEM = 0.71 (Korb et al., 2012; n = 199; mean age = 55.7 (14.6) years; HTN; French version; SEM calculated from given statistics)
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
Hypertension
- 1.98 (Muntner et al., 2011; HTN)
- 1.16 (Kim et al., 2014; MDC calculated from given statistics)
- 1.97 (Korb et al., 2012; MDC calculated from given statistics)
Cut-Off Scores
Hypertension (Morisky et al., 2008; n = 1367; mean age = 52.9 (12.2) years; HTN; Original English version)
Odds Ratios of Determinants of High Medication Adherence
Test/Retest Reliability
Hypertension
- Poor test-retest reliability (weighted kappa: 0.36; p< 0.001) (Okello et al., 2016; n = 329; mean age = 55 years; HTN; Runyankore/Rukiga version)
- Excellent test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.91) (Kim et al., 2014; n = 109; age not provided for subset; Korean version)
- Adequate test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.68) (Korbet al., 2012; French version)
Internal Consistency
Cardiovascular with polypharmacy (Arnet et al., 2015; n = 70; mean age = 65.7 (9.9) years; German version)
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.31)
Hypertension
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.54) (Korb et al., 2012; HTN; French version)
- Excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.83) (Morisky et al., 2008; HTN)
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.65) (Okello et al., 2016; HTN; Runyankore/Rukiga version)
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.56) (Kim et al., 2014, Korean version)
Criterion Validity (Predictive/Concurrent)
Predictive Validity:
Hypertension:
(Kim et al., 2014, HTN; Korean version)
- Sensitivity: 64.3% for predicting those with uncontrolled blood pressure (BP)
- Specificity: 72.9% for predicting those with controlled BP
- Positive predictive value: 29.5%
- Negative predictive value: 92.0%
- Relationship between adherence and BP control: Chi square = 29.86; p< 0.001; adjusted odds ratio = 5.08; 95% CI, 2.56–10.08
(Morisky et al., 2008)
- Sensitivity: 93% for predicting those with uncontrolled BP
- Specificity: 53% for predicting those with controlled BP
- Relationship between adherence and BP control: Chi-square: 6.6; p
Construct Validity
Convergent Validity:
Cardiovascular with polypharmacy (Arnet et al., 2015; German version)
- Adequate correlation between MMAS-8 (German) and Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire (BMQ): Necessity (r = 0.31; p< 0.01)
- Poor correlation between MMAS-8 and BMQ: Concerns (r = -0.16; p<0.05)
Hypertension
(Kim et al., 2014, HTN; Korean version)
- Excellent convergent validity between the MMAS-8 Korean version and the original 4-item Morisky, Green, & Levine Scale (r = 0.92; p< 0.01)
(Korb et al., 2012; HTN; French version)
- Factor analysis confirmed that the French MMAS was one-dimensional. Items 1, 2, 3, 4, and 8 had factor loadings >0.4. Item 8 had the highest correlation with the first component of the principal component analysis (r = 0.74), followed by item 1 (r = 0.70) and item 2 (r = 0.62).
- After adjustment for risk factors of low adherence, age was the only factor significantly associated with adherence. For each 10-year increase in age, the odds of having a lower adherence decreased by 25% (adjusted OR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.63–0.89; p =.001).
(Okello et al., 2016; Runyankore/Rukiga version)
- Factor analysis at baseline, using the Kaiser criterion, detected two factors, but tended to a one-factor solution (item 7). Item loadings ranged from 0.06 to 0.81. The overall Kaiser’s measure for sampling adequacy of residuals was 0.72.
Known Groups Validity:
Hypertension (Kim et al., 2014, HTN; Korean version)
Floor/Ceiling Effects
Hypertension (Kim et al., 2014, HTN; Korean version)
- Poor ceiling effect: The distribution of MMAS scores was skewed, median = 7.0 (range, 2.5–8.0). Ceiling effect was observed, as 34.0% of participants score = 8.0
Diabetes
Standard Error of Measurement (SEM)
Type 2 Diabetes (Sakthong et al., 2009; n = 303; mean age = 61.1 (11.4) years; T2DM, Thai version)
- SEM = 0.68 (calculated from given statistics)
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
Type 2 Diabetes (Sakthong et al., 2009; Thai version)
- 1.88 (calculated from given statistics)
Test/Retest Reliability
Type 2 Diabetes
- Excellent test-retest reliability (r = 0.82; p< .001) (Al-Qazaz et al., 2010; n = 175; mean age = 60.56 (9.16) years; minimum of 1-year post T2DM diagnosis; Malay version)
- Excellent test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.83; p< .001) (Sakthong et al., 2009; T2DM, Thai version)
Internal Consistency
Type 2 Diabetes
- Adequate internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.70) (Ashur et al., 2015; n = 103; mean age = 52.7 (8.6) years; Arabic version)
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.68) (Al-Qazaz et al., 2010; T2DM; Malay version)
- Poor internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.68) (DiBonaventura et al., 2014; T2DM; n = 1,198; mean age = 60.65 (10.74) years; currently using insulin glargine or insulin detemir)
Criterion Validity (Predictive/Concurrent)
Predictive Validity:
Type 2 Diabetes
(Ashur et al., 2015; T2DM; Arabic version)
- Sensitivity: 63.9% (95% CI 52.8-74%) for predicting those with poor HbA1c ( < 7%)
- Specificity: 82.3% (95% CI 56.5-96.2%) for predicting those with good HbA1c (>/= 7%)
(Al-Qazaz et al., 2010; Malay version)
- Sensitivity: 77.61% for predicting those with poor HbA1c ( < 7%)
- Specificity: 45.4% (95% CI 56.5-96.2%) for predicting those with good HbA1c (>/= 7%)
(Sakthong et al., 2009; Thai version)
- Sensitivity: 51% of diabetic patients who had poor glycemic control had low adherence
- Specificity: 64% of the patients with good blood glucose control were highly adherent to drug therapy
- Positive predictive value: 71% of subjects with low adherence were poorly controlled
- Negative predictive value: 43% of those with medium-to-high adherence had good glycemic control
Construct Validity
Convergent Validity:
Type 2 Diabetes
(Al-Qazaz et al., 2010; T2DM; Malay version)
- Excellent correlation between MMAS-8 (Malay) and Morisky Adherence Scale (r = 0.79; p< 0.01)
(Sakthong et al., 2009; Thai version)
Known Groups Validity:
Type 2 Diabetes
(Ashur et al., 2015; T2DM; Arabic version)
- Able to differentiate between diabetic patients with poor (HbA1c > 7%) and good (HbA1c > 7%) glycemic control with a moderate effect size (.34, p <.002)
(Sakthong et al., 2009; Thai version)
- A significant association between MMAS and A1C levels was found (Chi squared = 6.7;P < 0.05)
IRT-Based Validity:
Type 2 Diabetes (DiBonaventura et al., 2014)
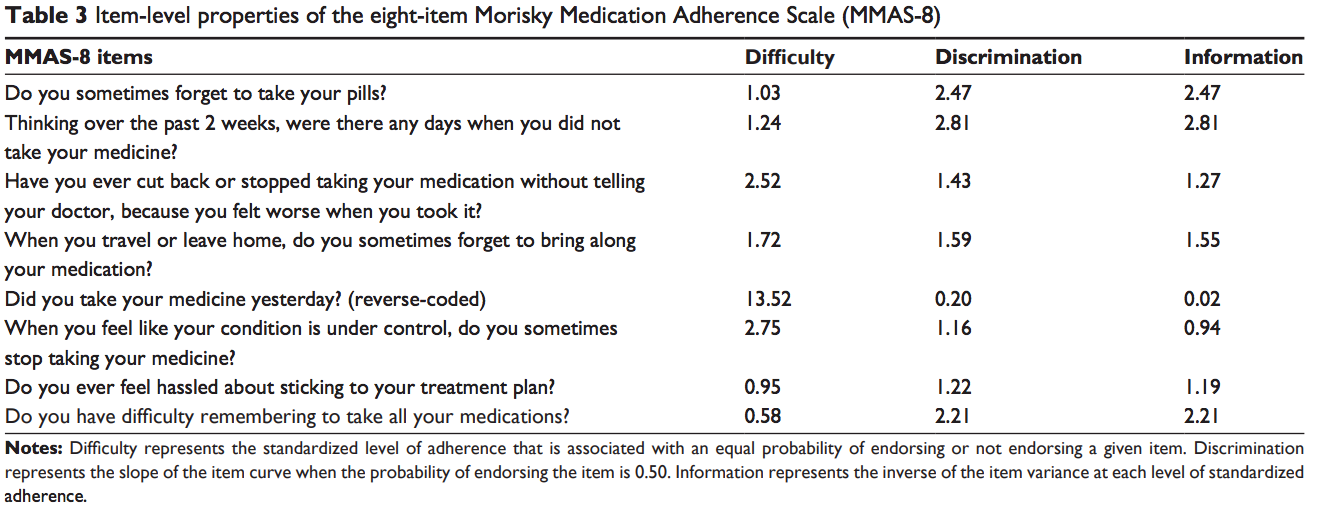
Bibliography
Al-Qazaz, H., Hassali, M., Shafie, A., Sulaiman, S., Sundram, S., & Morisky, D. (2010). The eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale MMAS: Translation and validation of the Malaysian version. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice, 90(2), 216-221.
Arnet, I., Metaxas, C., Walter, P., Morisky, D., & Hersberger, K. (2015). The 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale translated in German and validated against objective and subjective polypharmacy adherence measures in cardiovascular patients. Journal of Evaluation Practice, 21, 271-277.
Ashur, S.T., Shamsuddin, S.A., Bosseri, S., & Morisky, D.E. (2015). Reliability and known-group validity of the Arabic version of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 21(10), 722-728.
De las Cuevas, C., & Peñate, W. (2015). Psychometric properties of the eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in a psychiatric outpatient population. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 15, 121-129.
DiBonaventura, M., Wintfeld, N., Huang, J., & Goren, A. (2014). The association between nonadherence and glycated hemoglobin among type 2 diabetes patients using basal insulin analogs. Patient Preference and Adherence, 8, 873-882.
Kim, J-H., Lee, W-Y., Hong, Y-P., Ryu, W-S., Lee, K.J., Lee, W-S., & Morisky D.E. (2014). Psychometric properties of a short self-reported measure of medication adherence among patients with hypertension treated in a busy clinical setting in Korea. Journal of Epidemiology, 24(2), 132-140. doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20130064.
Korb-Savoldelli, V., Gillaizeau, F., Pouchot, J., Lenain, E., Postel-Vinay, N., Plouin, P-F.¸ . . . Sabatier, B. (2012). Validation of a French version of the 8-Item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in hypertensive adults. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 14(7), 429-434. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00634.
Morisky, D. E., Ang, A., KrouselWood, M., & Ward, H. J. (2008). Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 10(5), 348-354.
Morisky, D., & Turbow, S. (2017, Sept 30). MMAS Research. [website>. Retrieved from https://morisky.org/
Muntner, P., Joyce, C., Holt, E., He, J., Moriksy, D., Webber, L., & Krousel-Wood, M. (2011). Defining the minimal detectable change of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 45, 1-7. doi: 10.1345/aph.1P677
Okello, S., Nasasira, B., Wa Muiru, A. N., & Muyingo, A. (2016). Validity and reliability of a self-reported measure of antihypertensive medication adherence in Uganda. PLoS ONE, 11(7), 1-11.
Reynolds, K., Viswanathan, H., Muntner, P., Harrison, T., Craig Cheetham, T. Hsu, J-W., . . . O’Malley, O. (2014). Validation of the Osteoporosis-Specific Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in long-term users of bisphosphonates. Quality of Life Research, 23, 2109-2120.
Sakthong, P., Chabunthom, R., & Charoenvisuthiwongs, R. (2009). Psychometric properties for the Thai version of the 8-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in patients with type 2 diabetes. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 43(5), 950-957.
Tan, C., Teng, G., Chong, K., Cheung, P., Lim, A., Wee, H., & Santosa, A. (2016). Utility of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale in gout: a prospective study. Patient Preference and Adherence, 10, 2449-2457.
rehabilitation measures
More Instruments Like This
We have reviewed more than 500 instruments for use with a number of diagnoses including stroke, spinal cord injury and traumatic brain injury among several others.


