Data Link Controls

Data Link Control is the service provided by the Data Link Layer to provide reliable data transfer over the physical medium. For example, In the half-duplex transmission mode, one device can only transmit the data at a time. If both the devices at the end of the links transmit the data simultaneously, they will collide and leads to the loss of the information. The Data link layer provides the coordination among the devices so that no collision occurs.
The Data link layer provides three functions:
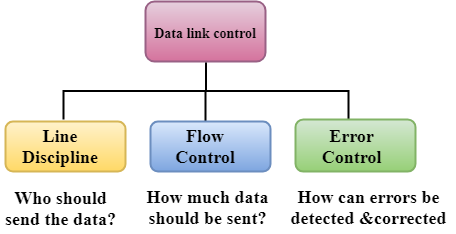
- Line discipline
- Flow Control
- Error Control
Line Discipline
- Line Discipline is a functionality of the Data link layer that provides the coordination among the link systems. It determines which device can send, and when it can send the data.
Line Discipline can be achieved in two ways:
END/ACK
END/ACK stands for Enquiry/Acknowledgement is used when there is no wrong receiver available on the link and having a dedicated path between the two devices so that the device capable of receiving the transmission is the intended one.
END/ACK coordinates which device will start the transmission and whether the recipient is ready or not.
Working of END/ACK
The transmitter transmits the frame called an Enquiry (ENQ) asking whether the receiver is available to receive the data or not.
The receiver responses either with the positive acknowledgement(ACK) or with the negative acknowledgement(NACK) where positive acknowledgement means that the receiver is ready to receive the transmission and negative acknowledgement means that the receiver is unable to accept the transmission.
Following are the responses of the receiver:
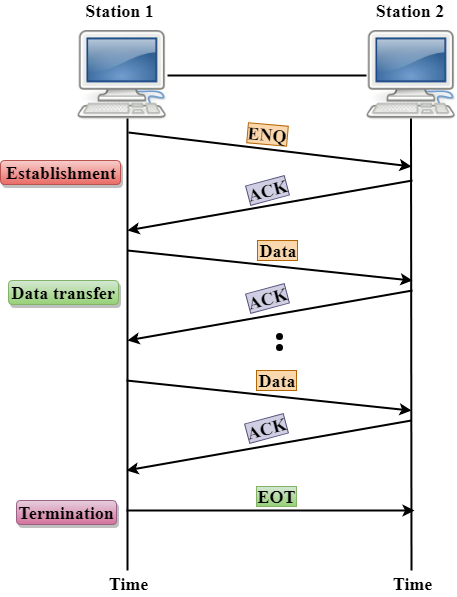
- If the response to the ENQ is positive, the sender will transmit its data, and once all of its data has been transmitted, the device finishes its transmission with an EOT (END-of-Transmission) frame.
- If the response to the ENQ is negative, then the sender disconnects and restarts the transmission at another time.
- If the response is neither negative nor positive, the sender assumes that the ENQ frame was lost during the transmission and makes three attempts to establish a link before giving up.
Poll/Select
The Poll/Select method of line discipline works with those topologies where one device is designated as a primary station, and other devices are secondary stations.
Working of Poll/Select
- In this, the primary device and multiple secondary devices consist of a single transmission line, and all the exchanges are made through the primary device even though the destination is a secondary device.
- The primary device has control over the communication link, and the secondary device follows the instructions of the primary device.
- The primary device determines which device is allowed to use the communication channel. Therefore, we can say that it is an initiator of the session.
- If the primary device wants to receive the data from the secondary device, it asks the secondary device that they anything to send, this process is known as polling.
- If the primary device wants to send some data to the secondary device, then it tells the target secondary to get ready to receive the data, this process is known as selecting.
Select
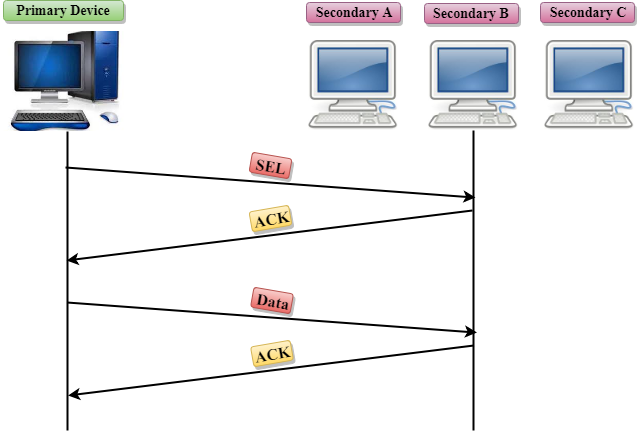
- The select mode is used when the primary device has something to send.
- When the primary device wants to send some data, then it alerts the secondary device for the upcoming transmission by transmitting a Select (SEL) frame, one field of the frame includes the address of the intended secondary device.
- When the secondary device receives the SEL frame, it sends an acknowledgement that indicates the secondary ready status.
- If the secondary device is ready to accept the data, then the primary device sends two or more data frames to the intended secondary device. Once the data has been transmitted, the secondary sends an acknowledgement specifies that the data has been received.
Poll
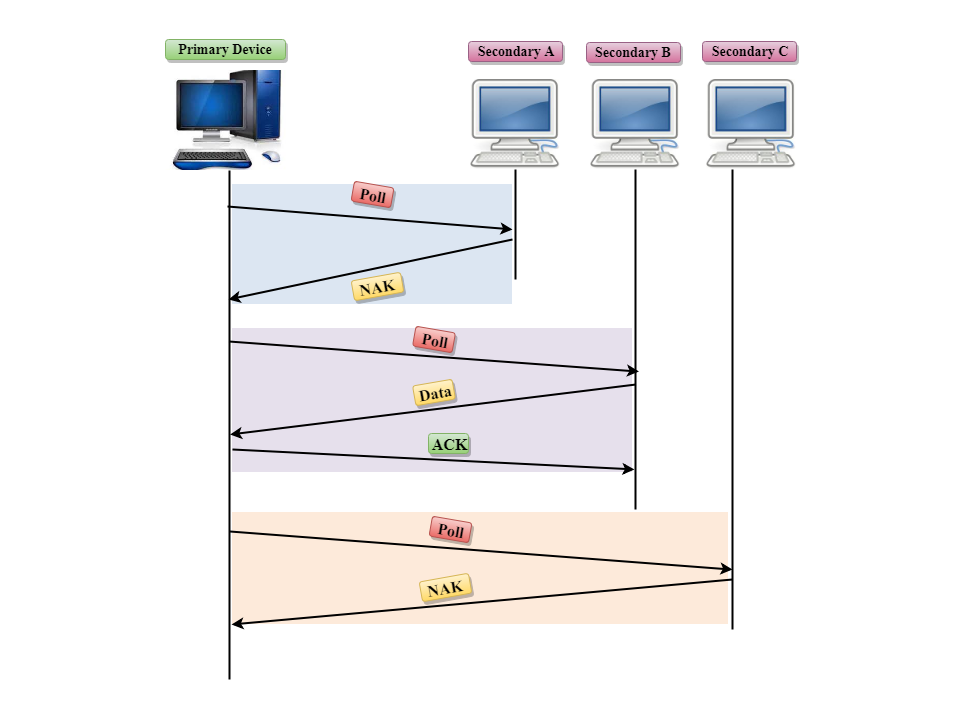
- The Poll mode is used when the primary device wants to receive some data from the secondary device.
- When a primary device wants to receive the data, then it asks each device whether it has anything to send.
- Firstly, the primary asks (poll) the first secondary device, if it responds with the NACK (Negative Acknowledgement) means that it has nothing to send. Now, it approaches the second secondary device, it responds with the ACK means that it has the data to send. The secondary device can send more than one frame one after another or sometimes it may be required to send ACK before sending each one, depending on the type of the protocol being used.
Flow Control
- It is a set of procedures that tells the sender how much data it can transmit before the data overwhelms the receiver.
- The receiving device has limited speed and limited memory to store the data. Therefore, the receiving device must be able to inform the sending device to stop the transmission temporarily before the limits are reached.
- It requires a buffer, a block of memory for storing the information until they are processed.
Two methods have been developed to control the flow of data:
- Stop-and-wait
- Sliding window
Stop-and-wait
- In the Stop-and-wait method, the sender waits for an acknowledgement after every frame it sends.
- When acknowledgement is received, then only next frame is sent. The process of alternately sending and waiting of a frame continues until the sender transmits the EOT (End of transmission) frame.
Advantage of Stop-and-wait
The Stop-and-wait method is simple as each frame is checked and acknowledged before the next frame is sent.
Disadvantage of Stop-and-wait
Stop-and-wait technique is inefficient to use as each frame must travel across all the way to the receiver, and an acknowledgement travels all the way before the next frame is sent. Each frame sent and received uses the entire time needed to traverse the link.
Sliding Window
- The Sliding Window is a method of flow control in which a sender can transmit the several frames before getting an acknowledgement.
- In Sliding Window Control, multiple frames can be sent one after the another due to which capacity of the communication channel can be utilized efficiently.
- A single ACK acknowledge multiple frames.
- Sliding Window refers to imaginary boxes at both the sender and receiver end.
- The window can hold the frames at either end, and it provides the upper limit on the number of frames that can be transmitted before the acknowledgement.
- Frames can be acknowledged even when the window is not completely filled.
- The window has a specific size in which they are numbered as modulo-n means that they are numbered from 0 to n-1. For example, if n = 8, the frames are numbered from 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,0,1.
- The size of the window is represented as n-1. Therefore, maximum n-1 frames can be sent before acknowledgement.
- When the receiver sends the ACK, it includes the number of the next frame that it wants to receive. For example, to acknowledge the string of frames ending with frame number 4, the receiver will send the ACK containing the number 5. When the sender sees the ACK with the number 5, it got to know that the frames from 0 through 4 have been received.
Sender Window
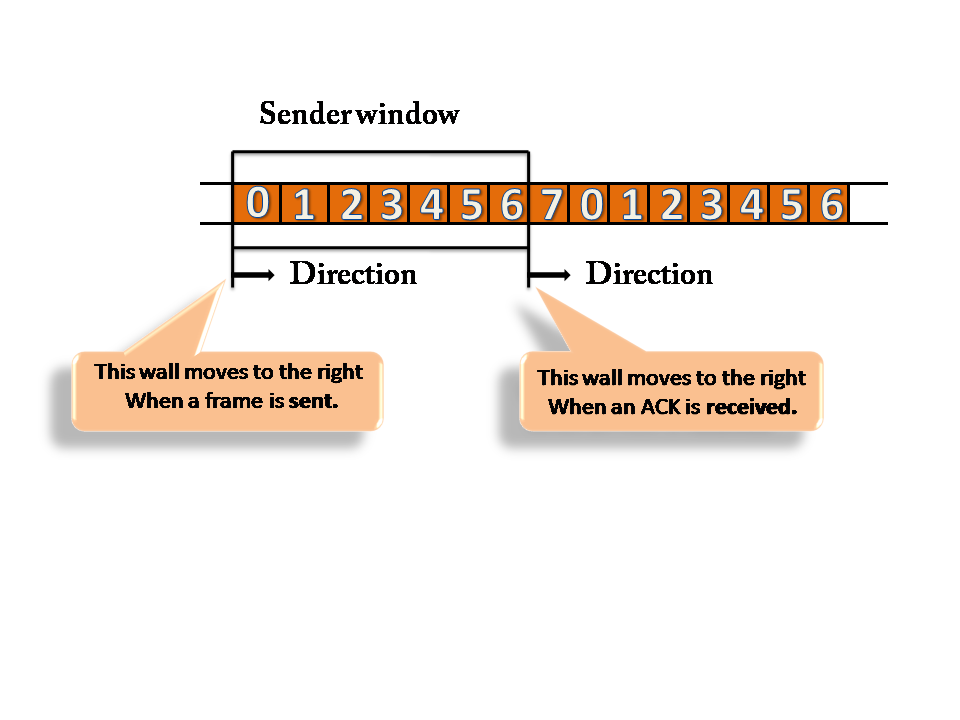
- At the beginning of a transmission, the sender window contains n-1 frames, and when they are sent out, the left boundary moves inward shrinking the size of the window. For example, if the size of the window is w if three frames are sent out, then the number of frames left out in the sender window is w-3.
- Once the ACK has arrived, then the sender window expands to the number which will be equal to the number of frames acknowledged by ACK.
- For example, the size of the window is 7, and if frames 0 through 4 have been sent out and no acknowledgement has arrived, then the sender window contains only two frames, i.e., 5 and 6. Now, if ACK has arrived with a number 4 which means that 0 through 3 frames have arrived undamaged and the sender window is expanded to include the next four frames. Therefore, the sender window contains six frames (5,6,7,0,1,2).
Receiver Window
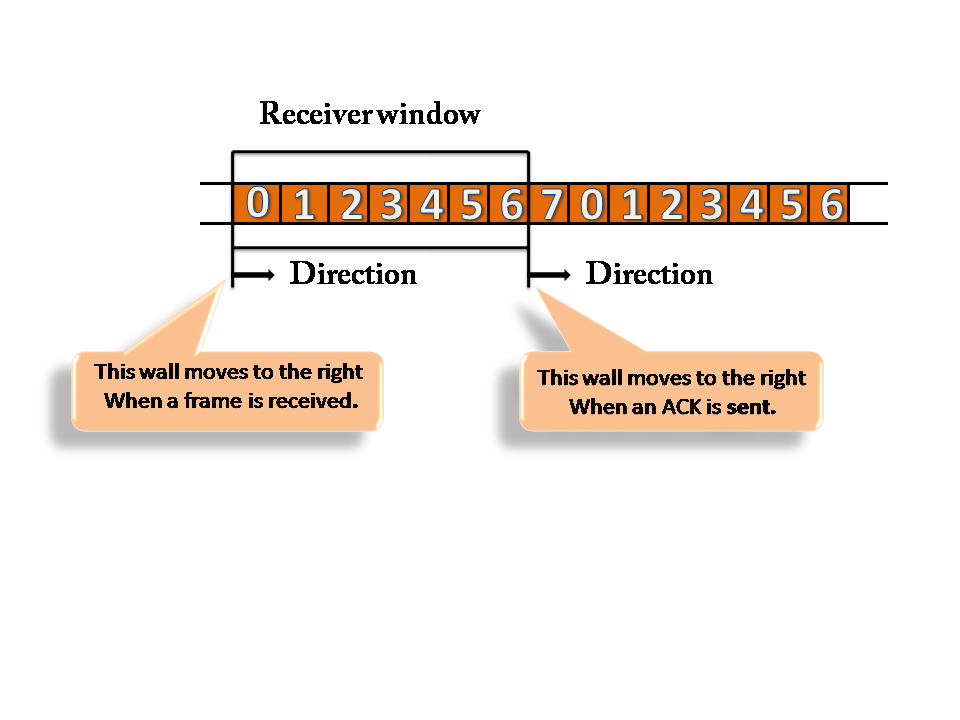
- At the beginning of transmission, the receiver window does not contain n frames, but it contains n-1 spaces for frames.
- When the new frame arrives, the size of the window shrinks.
- The receiver window does not represent the number of frames received, but it represents the number of frames that can be received before an ACK is sent. For example, the size of the window is w, if three frames are received then the number of spaces available in the window is (w-3).
- Once the acknowledgement is sent, the receiver window expands by the number equal to the number of frames acknowledged.
- Suppose the size of the window is 7 means that the receiver window contains seven spaces for seven frames. If the one frame is received, then the receiver window shrinks and moving the boundary from 0 to 1. In this way, window shrinks one by one, so window now contains the six spaces. If frames from 0 through 4 have sent, then the window contains two spaces before an acknowledgement is sent.
Error Control
Error Control is a technique of error detection and retransmission.
Categories of Error Control:

Stop-and-wait ARQ
Stop-and-wait ARQ is a technique used to retransmit the data in case of damaged or lost frames.
This technique works on the principle that the sender will not transmit the next frame until it receives the acknowledgement of the last transmitted frame.
Four features are required for the retransmission:
- The sending device keeps a copy of the last transmitted frame until the acknowledgement is received. Keeping the copy allows the sender to retransmit the data if the frame is not received correctly.
- Both the data frames and the ACK frames are numbered alternately 0 and 1 so that they can be identified individually. Suppose data 1 frame acknowledges the data 0 frame means that the data 0 frame has been arrived correctly and expects to receive data 1 frame.
- If an error occurs in the last transmitted frame, then the receiver sends the NAK frame which is not numbered. On receiving the NAK frame, sender retransmits the data.
- It works with the timer. If the acknowledgement is not received within the allotted time, then the sender assumes that the frame is lost during the transmission, so it will retransmit the frame.
Two possibilities of the retransmission:
- Damaged Frame: When the receiver receives a damaged frame, i.e., the frame contains an error, then it returns the NAK frame. For example, when the data 0 frame is sent, and then the receiver sends the ACK 1 frame means that the data 0 has arrived correctly, and transmits the data 1 frame. The sender transmits the next frame: data 1. It reaches undamaged, and the receiver returns ACK 0. The sender transmits the next frame: data 0. The receiver reports an error and returns the NAK frame. The sender retransmits the data 0 frame.
- Lost Frame: Sender is equipped with the timer and starts when the frame is transmitted. Sometimes the frame has not arrived at the receiving end so that it can be acknowledged neither positively nor negatively. The sender waits for acknowledgement until the timer goes off. If the timer goes off, it retransmits the last transmitted frame.
Sliding Window ARQ
SlidingWindow ARQ is a technique used for continuous transmission error control.
Three Features used for retransmission:
- In this case, the sender keeps the copies of all the transmitted frames until they have been acknowledged. Suppose the frames from 0 through 4 have been transmitted, and the last acknowledgement was for frame 2, the sender has to keep the copies of frames 3 and 4 until they receive correctly.
- The receiver can send either NAK or ACK depending on the conditions. The NAK frame tells the sender that the data have been received damaged. Since the sliding window is a continuous transmission mechanism, both ACK and NAK must be numbered for the identification of a frame. The ACK frame consists of a number that represents the next frame which the receiver expects to receive. The NAK frame consists of a number that represents the damaged frame.
- The sliding window ARQ is equipped with the timer to handle the lost acknowledgements. Suppose then n-1 frames have been sent before receiving any acknowledgement. The sender waits for the acknowledgement, so it starts the timer and waits before sending any more. If the allotted time runs out, the sender retransmits one or all the frames depending upon the protocol used.
Two protocols used in sliding window ARQ:
- Go-Back-n ARQ: In Go-Back-N ARQ protocol, if one frame is lost or damaged, then it retransmits all the frames after which it does not receive the positive ACK.
Three possibilities can occur for retransmission:
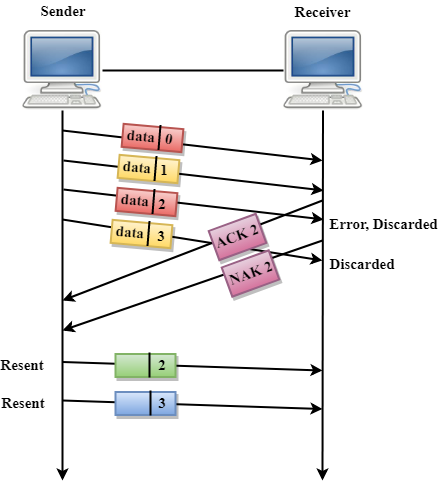
- Damaged Frame: When the frame is damaged, then the receiver sends a NAK frame.
In the above figure, three frames have been transmitted before an error discovered in the third frame. In this case, ACK 2 has been returned telling that the frames 0,1 have been received successfully without any error. The receiver discovers the error in data 2 frame, so it returns the NAK 2 frame. The frame 3 is also discarded as it is transmitted after the damaged frame. Therefore, the sender retransmits the frames 2,3.
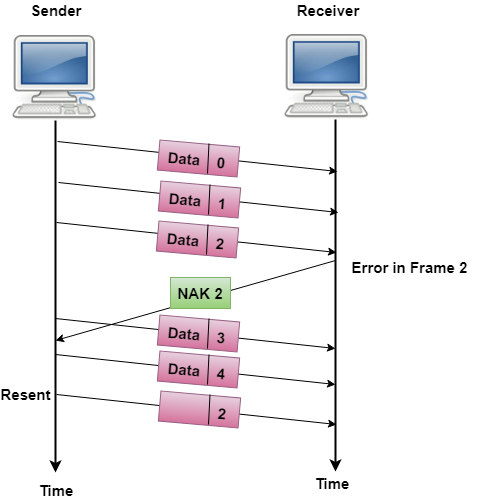
- Lost Data Frame: In Sliding window protocols, data frames are sent sequentially. If any of the frames is lost, then the next frame arrive at the receiver is out of sequence. The receiver checks the sequence number of each of the frame, discovers the frame that has been skipped, and returns the NAK for the missing frame. The sending device retransmits the frame indicated by NAK as well as the frames transmitted after the lost frame.
- Lost Acknowledgement: The sender can send as many frames as the windows allow before waiting for any acknowledgement. Once the limit of the window is reached, the sender has no more frames to send; it must wait for the acknowledgement. If the acknowledgement is lost, then the sender could wait forever. To avoid such situation, the sender is equipped with the timer that starts counting whenever the window capacity is reached. If the acknowledgement has not been received within the time limit, then the sender retransmits the frame since the last ACK.
Selective-Reject ARQ
- Selective-Reject ARQ technique is more efficient than Go-Back-n ARQ.
- In this technique, only those frames are retransmitted for which negative acknowledgement (NAK) has been received.
- The receiver storage buffer keeps all the damaged frames on hold until the frame in error is correctly received.
- The receiver must have an appropriate logic for reinserting the frames in a correct order.
- The sender must consist of a searching mechanism that selects only the requested frame for retransmission.
Next Topic

For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]











